Improving IT Service Management processes: The need for IT visibility
Modern IT environments are complex. Without proper IT visibility into such environments, optimizing IT service management processes is difficult. More so when you want to optimize them in line with ITIL process recommendations.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the ways IT visibility impacts IT service management processes. Especially in line with recommendations provided by ITIL processes (or practices). But before that let’s understand what IT visibility is followed by why ITIL process recommendation for IT service management matters.
IT Visibility: What it is and its importance
At its core, IT visibility entails having clear and accurate visibility into the performance, availability, and health of IT assets. At the same time, it also means the ability to monitor and analyze critical data points to extrapolate possibilities related to asset performance. It involves collecting and analyzing relevant data from diverse sources such as network devices, servers, applications, databases, logs, and user interactions.
The main components of IT visibility entail asset visibility, configuration visibility, and relationship visibility.
Asset visibility
Asset visibility includes having a real-time view of all tangible or intangible IT components that provide value. This includes hardware, software, networks, cloud services, IoT devices, and virtual environments.
- IT Visibility into hardware would mean knowing all the attributes of hardware and understanding its performance. But in the context of IT service management processes, it’s more about monitoring and tracking the health and status of physical devices. This includes storage systems, servers, and networking equipment.
- Visibility into software would mean understanding how different software components– operating systems, applications, databases, middleware, and services interact. Also, knowing their role in the overall system performance. It entails collecting and analyzing data on system performance, user behavior, and application usage.
- Network visibility would mean monitoring bandwidth usage, potential security vulnerabilities, and connectivity. This will ensure the highway that connects all the components of IT remains optimal for unceasing traffic.
Configuration visibility
Configuration visibility means having real-time insights into the configurations of various IT components. It enables IT teams to have a clear view of all the attributes and configuration items (CIs) that make up their IT environment. This visibility is important while carrying out changes, responding to incidents, or doing capacity planning.
Powered with automatic discovery tools such as Virima IT asset discovery, a CMDB can ensure accurate and up-to-date configuration information of IT assets. This includes information such as hardware specifications, software versions, network settings, security policies, access controls, and other relevant configuration parameters.
Relationship visibility
Relationship visibility, in terms of IT visibility, refers to the ability to understand and visualize how various IT components within an organization’s IT infrastructure relate and depend on one another. Apart from the large overview, relationship visibility shows the interconnectedness of various components in delivering a particular business service. Say, how components are responsible to keep the financial application running smoothly relates and depends on IT components for HR application.
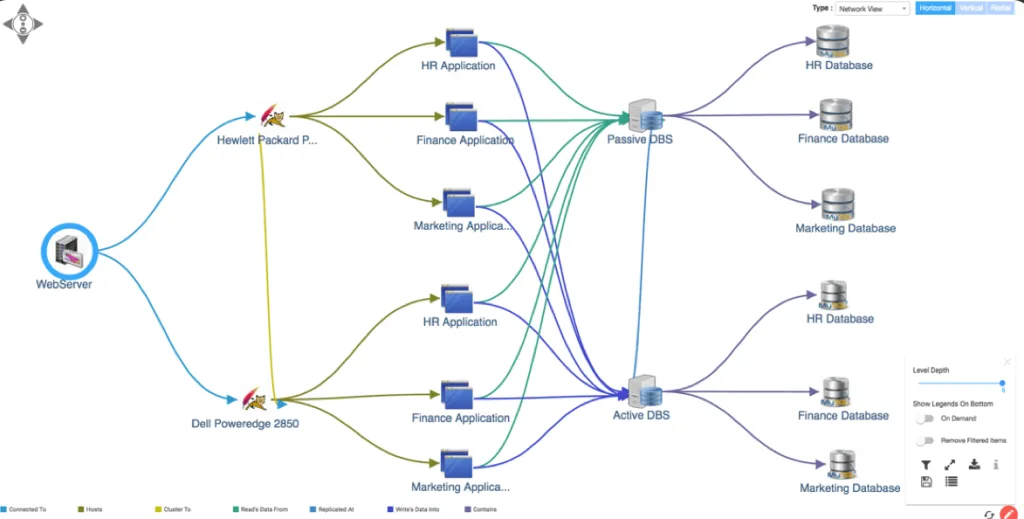
In this regard, Tools such as Virima service mapping provides multi-level visualization that helps in understanding the dependencies and impacts of changes or incidents on the overall system for every CI in the IT infrastructure.
ITIL practices for IT service management processes
ITIL processes are nothing but detailed practices designed to align IT services with business needs. When it comes to IT service management (ITSM), these processes provide guidance for designing and then delivering quality IT services. This includes change, incident, problem, and knowledge management services.
However, all this guidance isn’t specific to providing IT services for any singular technology or organization. Instead, the guidance through ITIL processes (now practices) can be used with any ITSM software or applied to knowledge management strategies for any organization providing IT services to customers or employees.
There were 26 ITIL processes (as per ITIL v3,2011) grouped into 5 stages of the service lifecycle. But in the latest ITIL 4, the ITIL processes are termed into ‘practices’. With a complete overhaul, ITIL 4 has 34 practices arranged into 3 management practice groups–General, Service, and Technical. Our concern is mainly with the service management practices group and how IT visibility helps implement them in the IT service management processes.
The Role of IT Visibility in Enhancing IT Service Management processes
The most prominent impact of IT visibility is seen in three IT service management practices- incident, problem, and change. So we’ll limit our scope of explanation to only those practices.
IT visibility for enhanced incident management processes
IT visibility can enhance all three stages of incident management– identification, diagnosis, and resolution. When an incident gets reported and the IT team opens the incident ticket, they can see the incident category, say Network. Now with the help of IT visibility provided by an ITAM tool, the IT team would get real-time information about the assets in the network infrastructure. This will include the status and configuration of routers, switches, and firewalls.
So if the reported incident concerned a sudden network outage affecting multiple services in an organization, the IT team can easily get right into the affected components. For example, ITAM provides information on the lifecycle of those assets, such as details on deployment, age, maintenance, and warranty. Using this information, the IT team can quickly decide whether to repair or replace the affected asset.
Moreover, while handling the issue, the relationship visibility provided by natively integrated ViVID service maps ensures the wider impact of resolving the incident is considered. For example, if a server failure is identified, IT visibility with service maps can determine which applications or services rely on that server. This will allow teams to quickly assess the potential impact.
Proactive incident resolution
ITIL process guidelines suggest taking measures to prevent incidents from occurring. In line with this recommendation, IT visibility helps in proactive incident resolution. It means even when an incident isn’t reported, the incident response processes will be in motion. It’s done through a number of ITAM features such as asset lifecycle management, capacity planning, and proactive security measures.
Asset lifecycle management, for instance, provides data on deployment, maintenance, procurement, and age, so insights from these data can be used to implement preventive maintenance, updates, or replacement. As a result of ITAM leads IT visibility, the likelihood of incidents caused by outdated or malfunctioning assets would be reduced.
Similarly, capacity planning can help IT teams proactively plan for capacity upgrades and avoid incidents caused by resource constraints.
IT visibility for root cause analysis and proactive problem management
As an essential aspect of IT service management, Problem management prevents the future occurrence of recurring incidents. For that, the first step is to identify the root causes of those recurring incidents. Then you need to find a way to prevent them from happening again.
Here service mapping tools help in the root cause analysis by providing a visual representation of the relationship and dependencies between assets and services.
Root cause analysis with service maps
An organization may want to find the root cause of unexpected downtime in their cloud-based file-sharing service. For that, the service map would provide a multi-level view of the entire IT infrastructure supporting the service. After testing their hypothesis, the IT team may find that the recent downtime coincides with a recent change in a network configuration. Going deeper levels in the service maps they can see the multiple servers connected to a network switch including the backup and file storage server.
By focusing their investigation on the network switch and its related components on the map, the IT team discovers that the recent configuration change inadvertently caused a loop in the network topology. This loop led to a broadcast storm that overwhelmed the network switch. As a result, it caused the file storage server to become inaccessible.
With the root cause identified, the IT team can now implement a solution to address the issue. It could be rolling back the configuration change or updating the network topology to prevent loops.
Proactive problem management
ITIL processes ( or ITIL 4 practices) call for proactive problem management. In this regard, ITSM tools such as ITIL-compliant Virima ITSM provides the necessary IT visibility into the incident management data. Here visibility means finding patterns in incidents by analyzing them to identify future or recurring problems.
However, this analysis should be based on complete and correct CI data from assets that experienced incidents. This requires a CMDB powered with an automated discovery that keeps CI data current and up-to-date.
IT visibility for streamlined change management processes
In change management, it’s critical to understand dependencies and relationships so that changes don’t inadvertently impact unrelated services. Service maps help by overlaying recent or pending changes, incidents, and existing dependencies. With the upgrade in Release Notes 5.11, we now offer live change overlays and auto-collision detection, enabling change managers to instantly view risk zones and dependencies before approving a change. This aligns strongly with ITIL’s principle of controlled, informed change decisioning.
Service maps greatly help in both understanding relationships and finding out potential change collisions. These maps overlay recently closed incidents or changes (and pending ones) in the infrastructure to help IT teams see the current state of assets and their dependencies. With the enhancements introduced in Release Notes 5.12, change managers can now view color-coded change severity overlays and “undo paths” directly on the map—making it easier to anticipate risks and rollback as needed.
These maps show the relationship and dependencies and bring out any potential change collisions. Moreover, these service maps overlay recently closed incidents or changes (and pending ones) in the infrastructure that the asset supports or is supported by. Hence the IT teams get to the current state of the assets or service relationships in question.
ITIL process recommendations (ITIL 4 practices) ask for an easy understanding of change collisions and current state visibility. This is to ensure decentralized change approvals and speedy impact assessment. The final objective is to carry out changes in the most informed and efficient manner.
Achieving enhanced IT service management processes with Virima ITAM
For incident management, Virima ITAM provides the required asset visibility. It does so in the form of configuration details for the assets, age, data on deployment, maintenance, warranty, and more. This information is complemented by the details on relationships and dependencies provided by ViVID service maps. Other features of ITAM such as asset lifecycle management and capacity planning, pave the way for proactive incident resolution.
The same ViVID service maps also help root cause analysis for problem management in line with the recommendations by ITIL processes. It also streamlines the change management process by providing easy visualization of possible change collisions and providing current relationship visibility.
The best thing about choosing Virima ITAM is that it comes natively integrated with exclusive ViVID service mapping.
Book a demo of Virima ITAM and experience enhanced IT visibility for IT service management in line with ITIL process recommendations.